Get In Touch
If you have any issues, or queries or facing any problems then you can contact us or leave us a message our team will get back to you as soon as possible.

Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a cutting-edge optical imaging technique that uses light waves to capture detailed images of your retina, the light-sensitive tissue lining the back of your eye. This non-invasive procedure allows us to view the multiple layers of your retina, enabling us to identify, diagnose, and treat potential abnormalities we find in your eye.
OCT is a significant advancement in the field of ophthalmology, providing a level of detail that was previously unattainable with traditional imaging methods.
The importance of Optical Coherence Tomography in eye health cannot be overstated. It provides a more detailed view of the retina than traditional eye examinations, revealing abnormalities and changes that might not be visible during a standard eye exam. This makes OCT an invaluable tool in the early detection and treatment of various eye conditions.
By allowing us to see beneath the surface of the retina, OCT provides a window into the health of your eyes, enabling us to catch potential issues before they become serious problems.
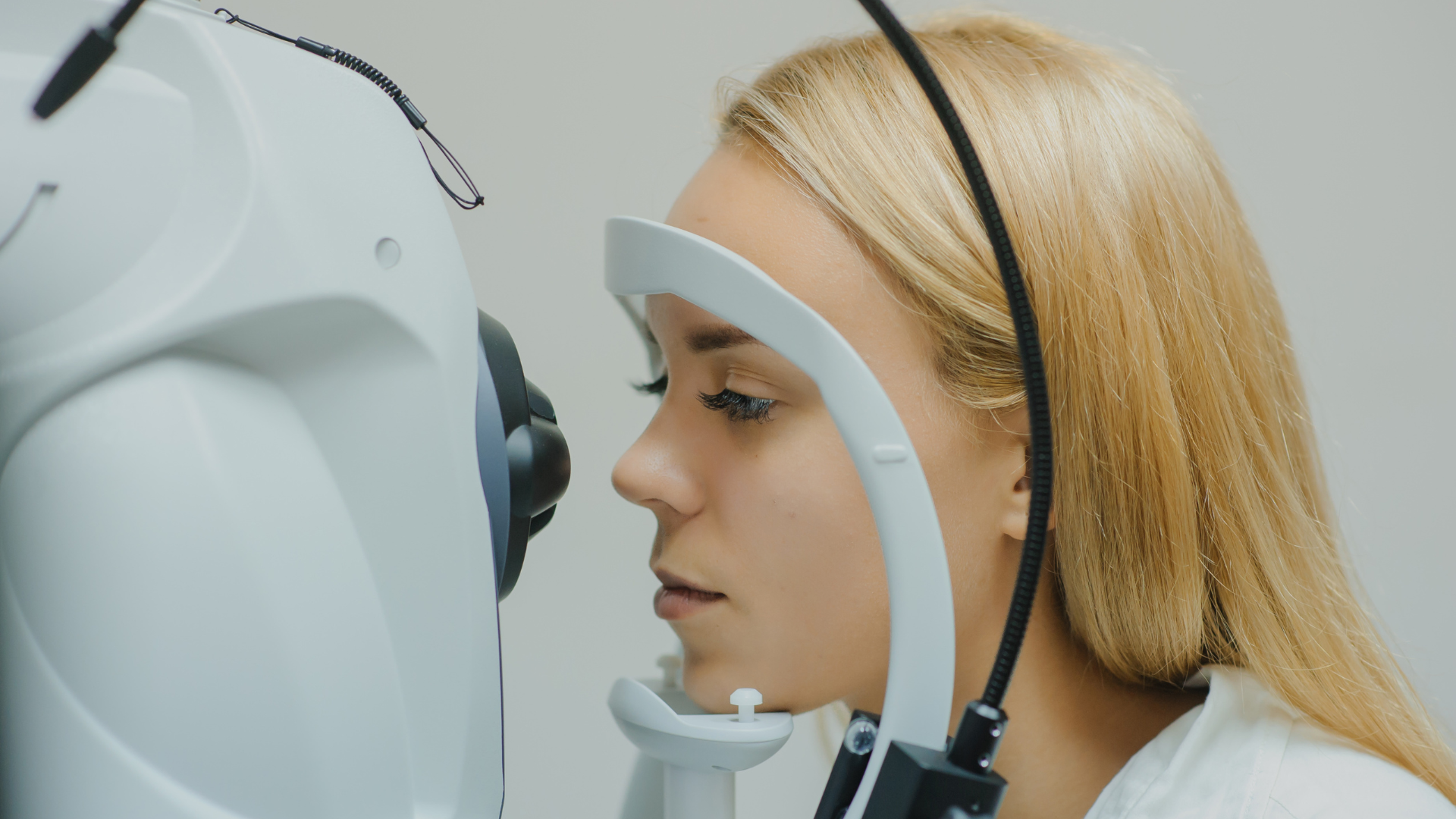
Undergoing an OCT scan is a simple and straightforward process. You may be asked to put some drops into your eye to dilate the pupil, which allows for a more comprehensive view of the retina. You’ll then rest your chin on a support and look into a small hole. The device scans your eye without touching it, a process that takes about 5 to 10 minutes.
Once the scan is complete, we can immediately review your results and discuss any findings. The entire process is quick, painless, and can provide a wealth of information about your eye health.
OCT allows us to examine the layers of your retina. This shows us any abnormalities, thickness, and any changes since your last appointment. This advanced imaging technique can help us detect and monitor a variety of health risks, including:
Changes caused by glaucoma: OCT can detect thinning of the nerve fibre layer that often precedes vision loss in glaucoma.
Damage to the optic nerve: OCT can reveal swelling or damage to the optic nerve, providing crucial information for diagnosing conditions like optic neuritis.
Diabetic retinopathy: OCT is crucial in diagnosing and managing diabetic retinopathy, a common complication of diabetes that can lead to blindness if left untreated.
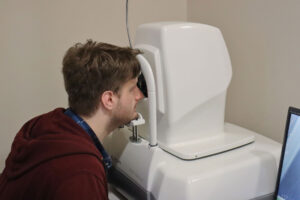

Rest assured, there are no significant risks associated with Optical Coherence Tomography. The only side effects that may occur are temporary dryness of the eye or eye fatigue. OCT uses low-intensity lasers to create an image of your eye, making it a safe procedure for most individuals.
No, OCT is a non-invasive and painless procedure. You may feel slight discomfort from the eye drops used to dilate your pupils, but the scan itself is painless.
The OCT scan itself usually takes about 5 to 10 minutes. However, if your pupils are being dilated, you may need to allow for additional time for the drops to take effect.
If your pupils were dilated for the OCT scan, your vision may be blurry and sensitive to light for a few hours. It’s generally recommended to have someone else drive you home after the procedure.
The frequency of OCT scans depends on your individual eye health and any conditions you may have. We can provide a personalised recommendation based on your needs.
While OCT is a powerful tool that can detect many eye conditions, it’s not a substitute for comprehensive eye exams. Regular eye exams are still essential for maintaining overall eye health.
Address :
111 Mostyn Street, Llandudno, LL30 2PD
info@garethrobertsopticians.co.uk
01492878176
9am-5.30pm
Copyright © 2023 Gareth Roberts Opticians